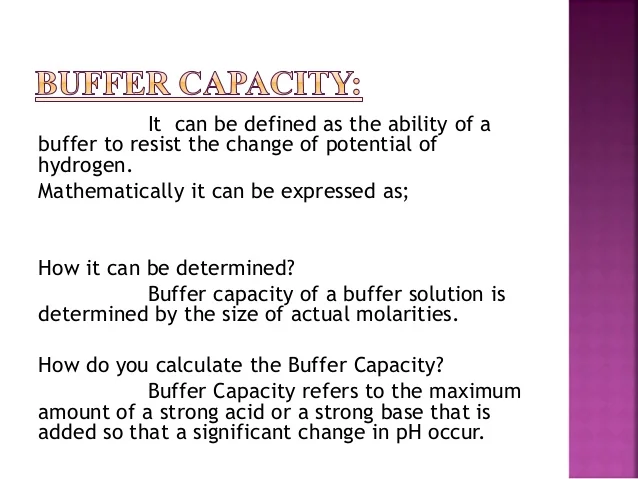
Buffer Solution Definition Chemistry
Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons. A buffer is an aqueous solution that has a highly stable pH.
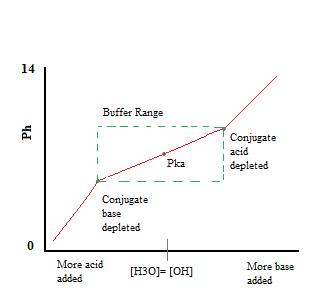
The buffer capacity can also be defined as the amount of mole of strong base needed to change the pH of 1 L of solution by 1 pH of unit.
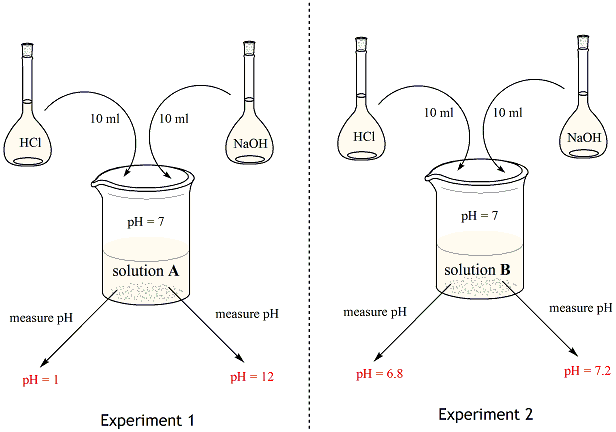
Buffer solution definition chemistry. A buffer is an aqueous solution that consists of a mixture of a weak acid and its salt acid buffer or a weak base with its salt basic buffer. Mixture of acetic acid CH 3 COOH and Sodium acetate CH 3 COONa in water. If you add an acid or a base to a buffered solution its pH will not change significantly.
A buffer is a compound that resists changes in pH when a limited amount of acid or base is added to it. This solution is quite important in the field of chemistry. A buffer may also be called a pH buffer hydrogen ion buffer or buffer solution.
In water solution sodium acetate is completely dissociated into sodium Na and acetate CH 3 COO - ions. A buffer solution is one which resists changes in pH when small quantities of an acid or an alkali are added to it. The chemical composition of a buffer solution usually entails a weak acid or a weak base accompanied by its conjugate salt.
Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications. Buffers are solutions that resist a change in pH on dilution or on addition of small amounts of acids or alkali. They resist a change in pH upon dilution or upon the addition of small amounts of acidalkali to them.
A buffer solution more precisely pH buffer or hydrogen ion buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa. Buffer in chemistry solution usually containing an acid and a base or a salt that tends to maintain a constant hydrogen ion concentration. A lot of biological and chemical reactions need a constant pH for the reaction to proceed.
A buffer solution refers to an aqueous solution. A buffer is a solution containing either a weak acid and its salt or a weak base and its salt which is resistant to changes in pH. Buffers are extremely useful in these systems to maintain the pH at a constant value.
Direct link to Melody Tans post A buffer solution is a solution that only changes. Furthermore it consists of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice-versa. In other words a buffer is an aqueous solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. The higher the acid concentration of the buffer then the buffer capacity will be higher as well. A buffering agent is a weak acid or weak base that helps maintain the pH of an aqueous solution after adding another acid or base.
Now Buffer Capacity can be defined as the measure of the efficiency of a buffer in resisting its change in pH. It is used to prevent any change in the pH of a solution regardless of solute. Buffer solution and examples in chemistry.
A buffer solution is a solution that only changes slightly when an acid or a base is added to it. An example of a common buffer is a solution of acetic acid CH 3 COOH and sodium acetate. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it.
This does not mean that the pH of buffers does not change. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it and is thus used to prevent a solution s pH change. In chemistry buffer solution and examplesIt is a solution containing either a weak acid and its salt or a weak base and its salt which resists changes in pH.
A buffers pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. The buffer capacity is a quantity in resisting the pH change at the time of addition of an acid or base. For an acid-buffer solution it consists of a week acid and its conjugate base.
In other words a buffer is an aqueous solution of either a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. Posted 3 years ago. A solution which resists the change in its pH value even on the addition of a small amount of strong acid or base is called a buffer solution or buffer.
A buffer is an aqueous solution containing a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. This is important for processes andor reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges. Buffer Solution is a water solvent based solution which consists of a mixture containing a weak acid and the conjugate base of the weak acid or a weak base and the conjugate acid of the weak base.
You can explore more about buffer solutions here. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable.
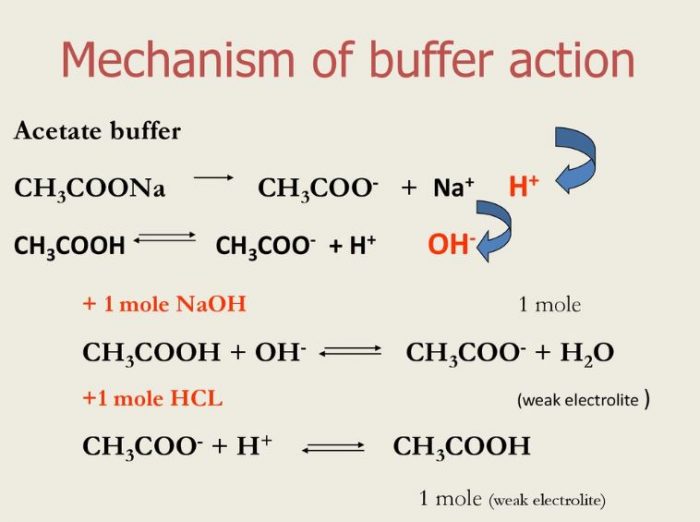 Buffer Solution And Buffer Action Chemistry Class 11 Ionic Equilibrium
Buffer Solution And Buffer Action Chemistry Class 11 Ionic Equilibrium
 Buffer Solutions Biochemistry The Biology Notes
Buffer Solutions Biochemistry The Biology Notes
 Examples Of Buffer Solution In Everyday Life Their Applications And Uses
Examples Of Buffer Solution In Everyday Life Their Applications And Uses
 A Buffered Vs A Non Buffered Solution Chem13 News Magazine University Of Waterloo
A Buffered Vs A Non Buffered Solution Chem13 News Magazine University Of Waterloo
 Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
 Buffer Solution Its Characteristics Types And Preparations
Buffer Solution Its Characteristics Types And Preparations
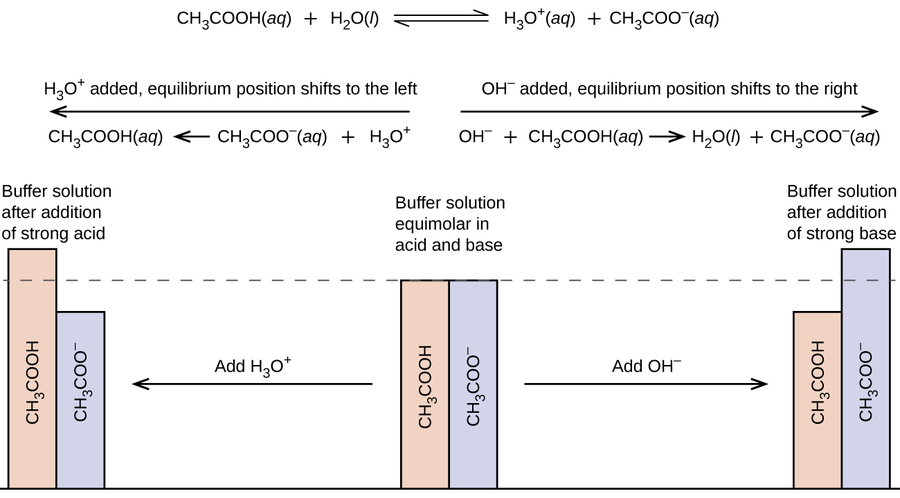 7 1 Acid Base Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
7 1 Acid Base Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
 Buffer Solutions Study Material For Iit Jee Askiitians
Buffer Solutions Study Material For Iit Jee Askiitians
Buffers Indicators Acids And Bases 101 The Basics Of Chemistry
 Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
 18 2 1 Describe The Composition Of A Buffer Solution And Explain Its Action Youtube
18 2 1 Describe The Composition Of A Buffer Solution And Explain Its Action Youtube
Buffer Solution Solution Of Reserve Acidity Alkalinity
 Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy
Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy
 Buffer Solution Ph Calculations Video Khan Academy
Buffer Solution Ph Calculations Video Khan Academy
 Buffer Capacity Chemistry Definition And Formula Az Chemistry
Buffer Capacity Chemistry Definition And Formula Az Chemistry
 Buffer Capacity Video Buffer Solutions Khan Academy
Buffer Capacity Video Buffer Solutions Khan Academy