Define Buffer Pharmacology
The basic form will be protonated and have less hydrogens to be able to neutralize acids. An excipient is a substance formulated alongside the active ingredient of a medication included for the purpose of long-term stabilization bulking up solid formulations that contain potent active ingredients in small amounts thus often referred to as bulking agents fillers or diluents or to confer a therapeutic enhancement on the active ingredient in the final dosage form such as.
Tablet or gelatine capsule breaks up into smaller particles.
Define buffer pharmacology. A buffer system is a solution that resists a change in pH when acids or bases are added. The content breaks up into small granules which then disaggregate. Any substance upon which an enzyme acts.
Covers all currently marketed drugs with their chemical data and diagrams. Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary Farlex 2012 pK a The negative decadic logarithm of the ionization constant K a of an acid. Terms in this set 9 Brand.
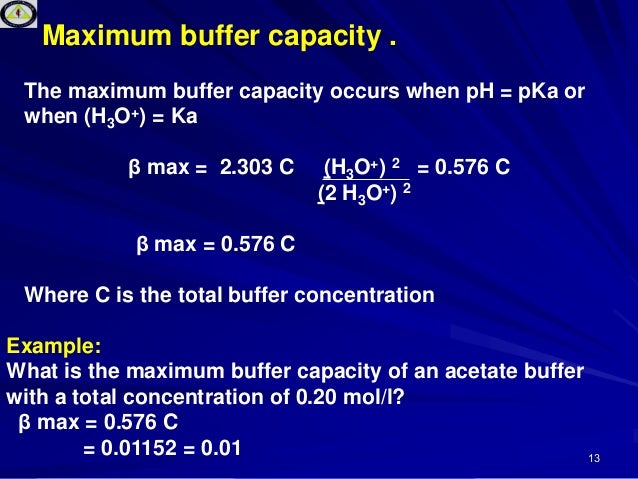
Equal to the pH value at which equal concentrations of the acid and conjugate base forms of a substance often a buffer are present. Recognize the various types of buffer solutions and their methods of preparation. The buffering capacity of a species or its ability to maintain pH of a solution is highest when the pKa and pH values are close.
Calculate the quantity of ingredients needed to prepare a buffer solution. To define the chemistry of this putative two-electron TH redox cycle we studied the hydrolysis and reduction of 8a-24-dimethyl-1-nitrilopent-2-yldioxytocopherone 1 in acetonitrilebuffer mixtures and in phospholipid liposomes. Buffers are used in pharmaceutical products for 2 puposes.
Dictionary of Drugs -- In CHEMnetBASE choose Dictionary of Drugs from the images. To adjust the pH of product for maximum stability. Definition of a Buffer which you can easily find in every book or site is.
How to use buffer in a sentence. A high collapse temperature would facilitate a faster primary drying and its non-volatile nature. Buffer solutions are solutions that resist changes in pH upon addition of small amounts of acid or base or upon dilution.
Define a buffer solution and list its components. A surface upon which a different material is deposited or adhered usually in a coating or layer. It usually takes place in two steps.
Here we discuss the physiological processes which determine and regulate the pH of the extracellular fluid and thus the blood pH. PKa Definition in Chemistry. Pre-existing metabolic acidosis ASA and cyclic.
The acidic form of a buffer will have more hydrogens to be able to neutralize hydroxy groups. Which two factors determine the effectiveness of a buffer. Buffer and its concentration is important for sensitive molecules.
Buffer definition is - fellow man. PH pKa log baseacid. Experimental sciences include biochemistry pharmacology and physics as well as in homeopathy.
Helmenstine Anne Marie PhD. Buffers contain a weak or medium strong acid base and the corresponding salt. And compounds in later stages of clinical trials.
Disintegration is a physical process that occurs when a dosage form eg. Calculate the pH of a buffer solution. The skin possesses a fairly high buffer capacity which is determined by the amount of H or OH- ions that is needed until the pH value of a solution changes by the unit 1.
Paramedic Pharmacology - Sodium Bicarbonate. Define and calculate the buffer capacity of a buffer solution. Serial dilution is the stepwise dilution of a substance in solution.
Dictionary of Cancer Terms-- From the National Cancer Institute NCI. So when selecting a buffer the best choice is the one that has a pKa value close to the target pH of the chemical solution. Drug profile for sodium bicarbonate.
A neutral substance containing a nutrient solution. Although this section is categorized under Renal Medicine respiratory processes are key players in the regulation of acid-base balance. A method used to stepwise dilute substance into solution with constant dilution factor in each step.
The pH of a buffer in the blood can be determined by pH pK log acidbase pH pK log baseacid pH 70 log baseacid pH pK log baseacid pH 74 - log baseacid 12. The buffering agent should have a high collapse temperature be non-volatile and have a high glass transition temperature Tg. Buffers hydrogen ions and increase pH.
In chemistry biochemistry and pharmacology a dissociation constant is a specific type of equilibrium constant that measures the propensity of a larger object to separate dissociate reversibly into smaller components as when a complex falls apart into its component molecules or when a salt splits up into its component ionsThe dissociation constant is the inverse of the association constant.
Http Courseware Cutm Ac In Wp Content Uploads 2020 06 Role Of Buffers In Pharmacy Pdf
 What Is Pharmacology Definition Principles Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
What Is Pharmacology Definition Principles Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
 Ppt Safety Pharmacology Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 3346708
Ppt Safety Pharmacology Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 3346708
 Buffer Solution Types Buffer Capacity Inorganic Pharma Chemistry Youtube
Buffer Solution Types Buffer Capacity Inorganic Pharma Chemistry Youtube
 Buffer And Extraction Buffer Biochemistry Microbe Notes
Buffer And Extraction Buffer Biochemistry Microbe Notes
Https Www Kgmu Org Download Virtualclass Physiology L9 10 Basics Of Acid And Base Pdf
 Commonly Used Instruments In Experimental Pharmacology
Commonly Used Instruments In Experimental Pharmacology
Defining And Understanding Strength Training Load Progression Human Kinetics Canada
 Semi Solid Dosage Form Definition Advantage Disadvantage Ingredients Imdip India S First Website On Pharmacy
Semi Solid Dosage Form Definition Advantage Disadvantage Ingredients Imdip India S First Website On Pharmacy
 Pdf Buffers And Ph Adjusting Agents
Pdf Buffers And Ph Adjusting Agents
 Buffered Solutions Buffer Capacity Pharma Mirror Magazine
Buffered Solutions Buffer Capacity Pharma Mirror Magazine
What Is The Role Of A Buffer In A Pharmacy Quora
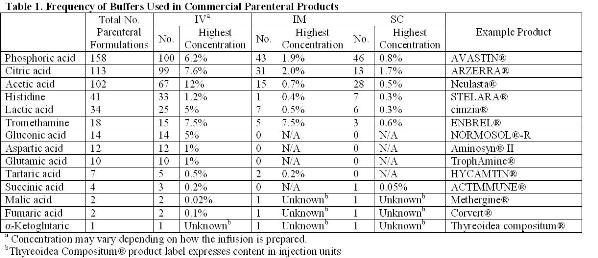 Breaking Old Habits Moving Away From Commonly Used Buffers In Pharmaceuticals European Pharmaceutical Review
Breaking Old Habits Moving Away From Commonly Used Buffers In Pharmaceuticals European Pharmaceutical Review
 Buffers And Henderson Hasselbalch Video Khan Academy
Buffers And Henderson Hasselbalch Video Khan Academy
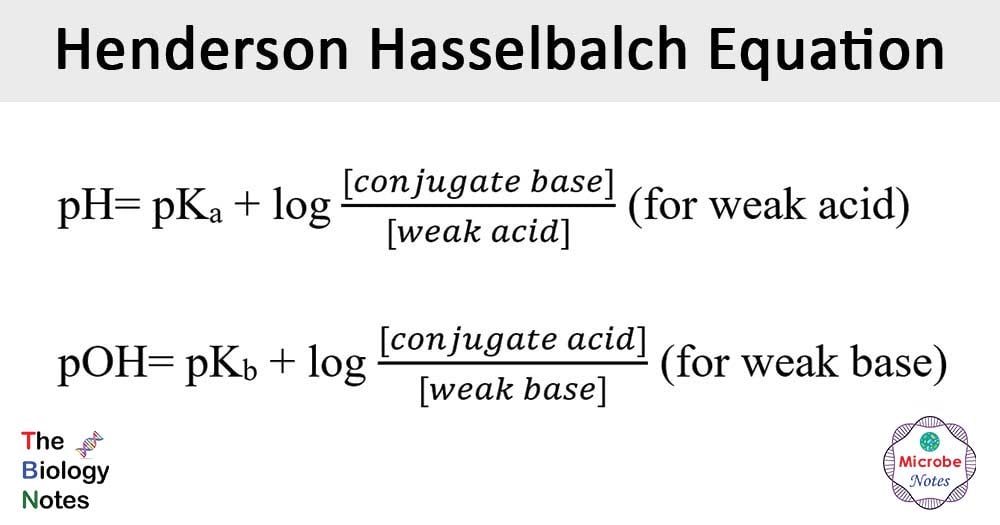 Henderson Hasselbalch Equation Microbe Notes
Henderson Hasselbalch Equation Microbe Notes